|
Computer-controlled data acquisition systems (that is,
computer hardware and software system used to collect real world scientific data) are
typically self-contained systems accessible only to investigators physically present at
the data collection site. However, distributed computing technology allows access such
systems througth computer networks, supporting both remote observation of experiments and
remote control of hardware and software.
Remote observation is valutable whether it
takes place in "real time" mode (that is, collected in the experiment is
streamed to the remote site) or in the "store-and-forward" mode (the collected
data is stored as a file then sent asynchronously to the remote site). The several
mode is particularly useful when coordinating remote viewers over several time zones with
a collection site. However, certain kinds of data, experiment on the particular scientific
support, are most meaningful when viewed in real time, so a store-and-forward data
acquisition system should support a "playback" mode, in which remote observers
can recrate the original data collection.
No matter which mode is used, distributed data
acquisition makes possible the collection of data from extreme environments (such as
space), and can also improve collaboration among geographically dispersed scientific
communities by distributin scientific results more quickly and less expensively than most
other methods. However, problems arise when the acquired data is of a sensitive or
classified nature and must be protected from unauthorized viewing. Private networks based
on satellite technology or "closed-path" nethworks can protect distributed
data's confidentiality, but such networks are expensive to create and difficult to
maintain. Public networks, the most videly used of which is the Internet , are less
expensive, widely accessible, and easy for non-expert to use, but they are
notoriously insecure. While mechanisms would affect the acquisiton ad delivery of
scientific data to remote observers.
The Automatic Control Telelab, support
real-time configuration and observation of experiments, as well as playback access to
acquired data, from remote computer linked to a collection site through the Internet.
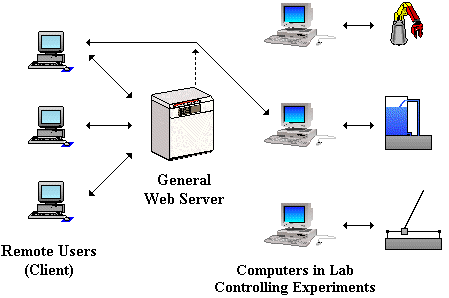
Architecture of the Automatic Control Telelab
|